

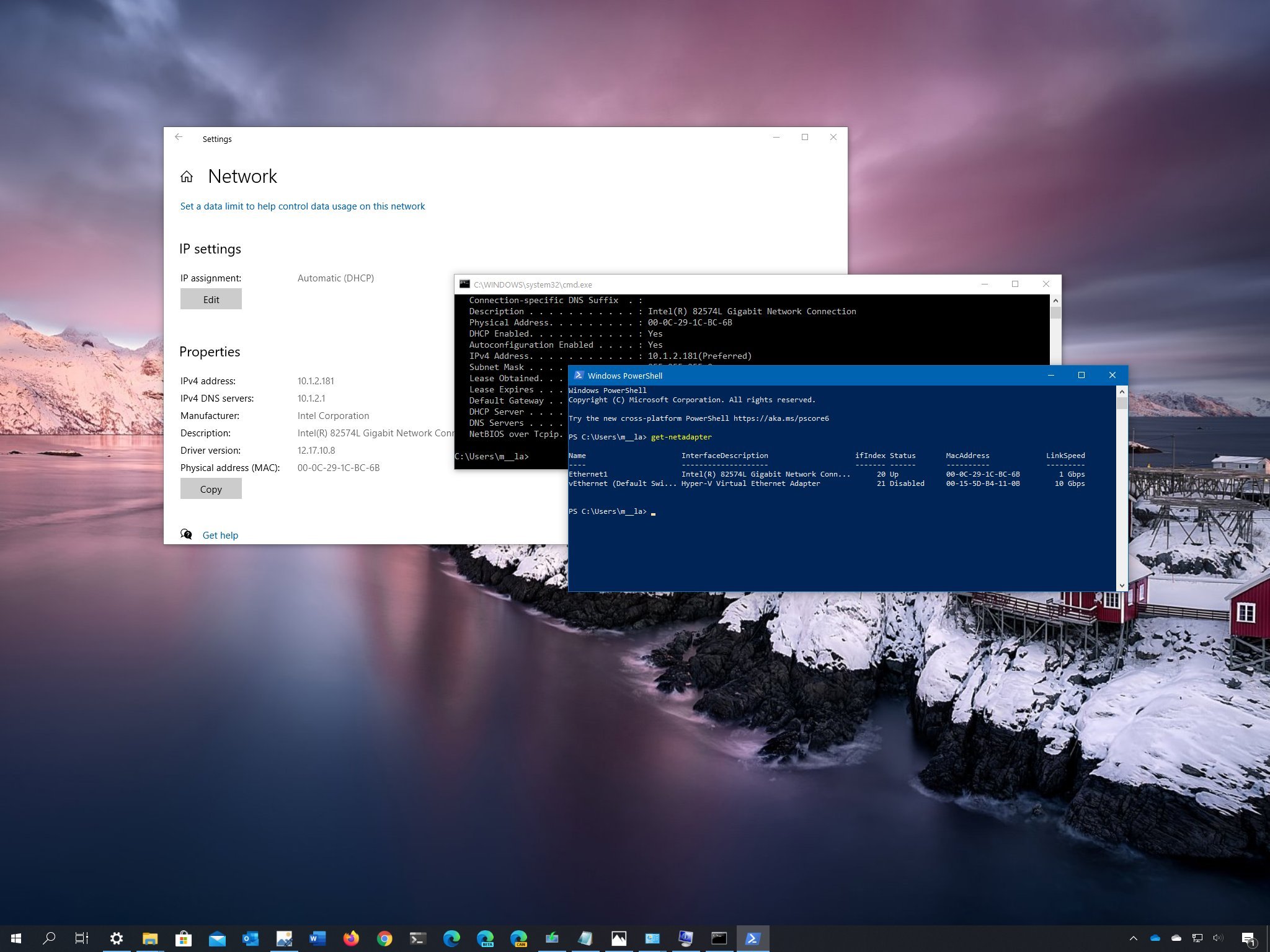
This is your device’s MAC address.Ī Wi-Fi Address displays. Select Apple Icon > System Preferences > Network > Advanced.Ī WiFi Address or Airport Address displays.This is your computer’s Ethernet MAC address. Under Ethernet adapter Wireless Network Connection, a Physical Address displays. In the command prompt, type ipconfig /all.The physical address is your device’s MAC address.
For vpn do i need mac address of workstation or router windows#
Click Windows Start or press the Windows key.Ī physical address displays for each adapter.You can block or allow service to a specific device if you know its MAC address.Ĭlick the link for your operating system: If your computer has multiple network adapters (for example, an Ethernet adapter and a wireless adapter), each adapter has its own MAC address. Follow the steps for the operating system that you use.Įxample of a MAC address: 00:00:00:a1:2b:ccĮvery device connected to your home network has a unique MAC address. For getting the addressing information on specific interfaces ip -o -4 addr can be used and ip route can be used for getting routing/gateway information.Follow these instructions to find your computer or mobile device’s media access control address (MAC address).
/desk-computer-macbook-apple-working-table-764627-pxhere.com-32891446593849699295941dcc12713a.jpg)
According to pilona's and Gilles's answers on Difference between 'ifconfig' and 'ip' commands, Linux kernel and networking features have advanced forward but ifconfig and the package to which it belongs haven't evolved in a long time, and that's why we have ip utilities. there's set of lines for one interface, then separated by a blank line another set of lines and so forth.Īnother alternative that one can use would be ip command which is preferred nowadays to ifconfig. With nmcli information is shown in accordance with each interface, i.e. Here's alternative to the above: $ nmcli dev show | grep 'IP4\.ADDRESS\|IP4.GATEWAY' It should be noted, however, that nmcli before and after 15.04 differs with several command-line arguments. Rinzwind's answer on the related question has cited the changelog for Network Manager package, which explains that it has been dropped upstream and superseded by nmcli. This small utility would interface nicely with the Network Manager and produce a report with appropriate information on each line, which was quite simple to parse with text processing utilities. The nm-tool utility provides information about NetworkManager, device, and wireless networks. Nm-tool - utility to report NetworkManager state and devices In versions before 15.04 there used to exist nm-tool utility. Here's this network: 255.255.255.224 is the netmask, add up the "1" bits: Often, you'll see networks described with a /. Now you're wanting to set up an ubuntu firewall and need to set up your public interface: Calculate network IP address:Ģ55.255.255.224 : E0 -> there are 1F = 31, In reality, most people call "the network" anything with ethernet cables that can talk to each other.Įxample: your ISP gives you info to type into a wireless router: a static IP address of 99.1.81.209 and your netmask is 255.255.255.224. To get to " the network", the network address is used. " The network" typically means everyone above you, including the Internet. The " range of ip addresses left over from the netmask" is known as the local network. broadcast is the highest numbered ip address in that range. To simplify that article: network is the lowest possible address in the range of ip addresses left over from the netmask. This website explains how the network and broadcast addresses can be calculated via a netmask and a computer's ip address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
